the 4Cs of Diamond Quality is the universal method for assessing the quality of any diamond.
A Diamond's Cut Unleashes Its Light. Diamonds are renowned for their ability to
transmit light and sparkle so intensely. We often think of a diamond's cut as shape
(round, emerald, pear), but a diamond's cut grade is really about how well a
diamond's facets interact with light.
Precise artistry and workmanship are
required to fashion a stone so its proportions, symmetry, and polish deliver the
magnificent return of light only possible in a diamond.

A diamond's cut is crucial to the stone's final beauty and value. And of all the diamond 4Cs, it is the most complex and technically difficult to analyze.

To determine the cut grade of the standard round brilliant diamond - the
shape
that
dominates the majority of diamond jewelry – GIA calculates the proportions
of
those
facets that influence the diamond's face-up appearance. These proportions
allow
GIA
to evaluate how successfully a diamond interacts with light to create
desirable
visual effects such as:
Brightness: Internal and
external
white light reflected from a diamond
Fire: The
scattering
of white light into all the colors of the rainbow
Scintillation: The amount of sparkle a diamond produces,
and
the
pattern of light and dark areas caused by reflections within the diamond
GIA's diamond cut grade also takes into account the design and craftsmanship
of
the
diamond, including its weight relative to its diameter, its girdle thickness
(which
affects its durability), the symmetry of its facet arrangement, and the
quality
of
polish on those facets.
The GIA Diamond Cut Scale for standard
round
brilliant diamonds in the D-to-Z diamond color range contains 5 grades
ranging
from
Excellent to Poor.
Diamond carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond weighs. A metric
"carat" is defined as 200 milligrams.
Each carat can be subdivided into 100
'points.' This allows very precise measurements to the hundredth decimal place. A
jeweler may describe the weight of a diamond below one carat by its 'points' alone.
For instance, the jeweler may refer to a diamond that weighs 0.25 carats as a
'twenty-five pointer.' Diamond weights greater than one carat are expressed in
carats and decimals. A 1.08 carat stone would be described as 'one point oh eight
carats.'
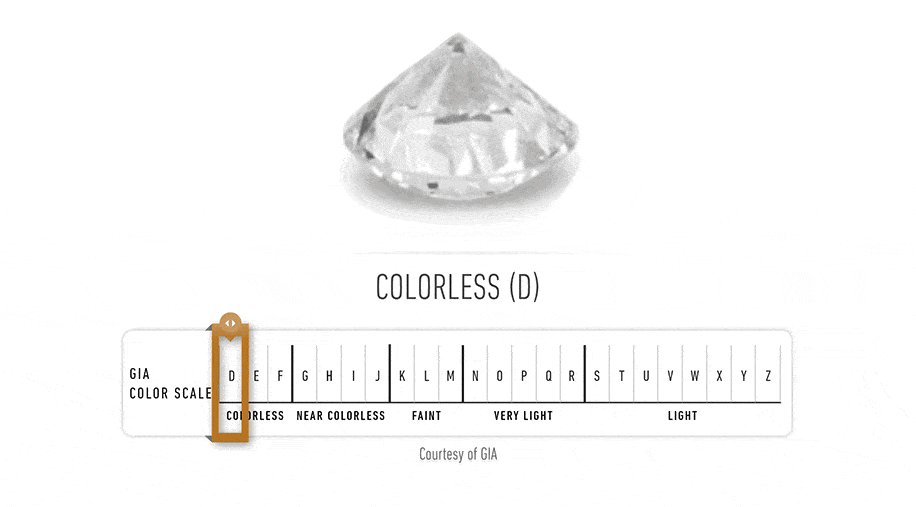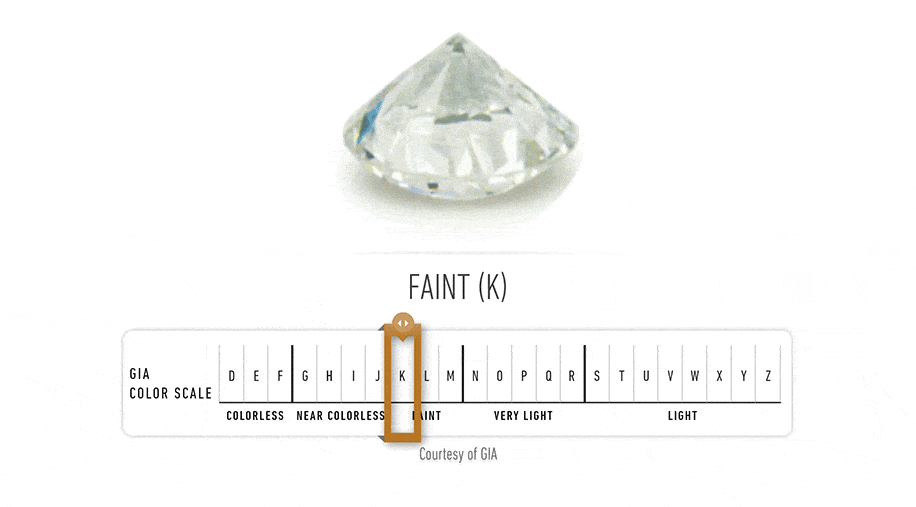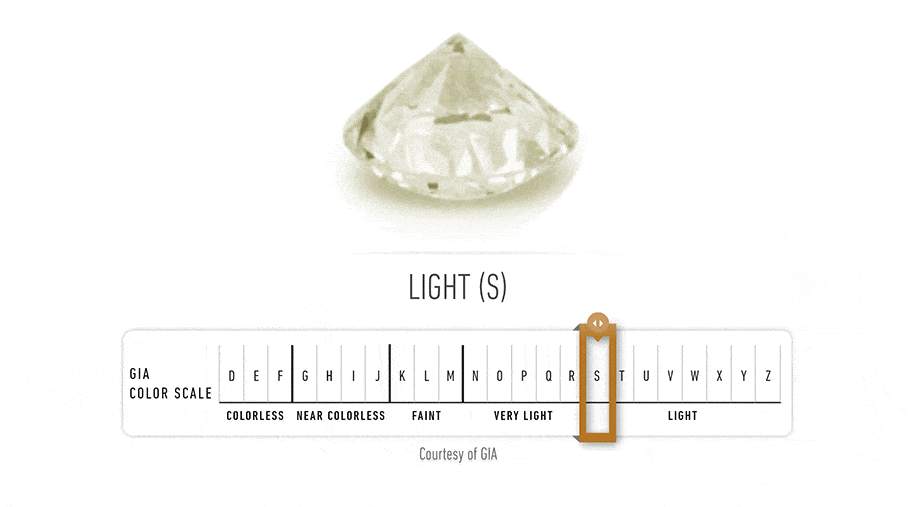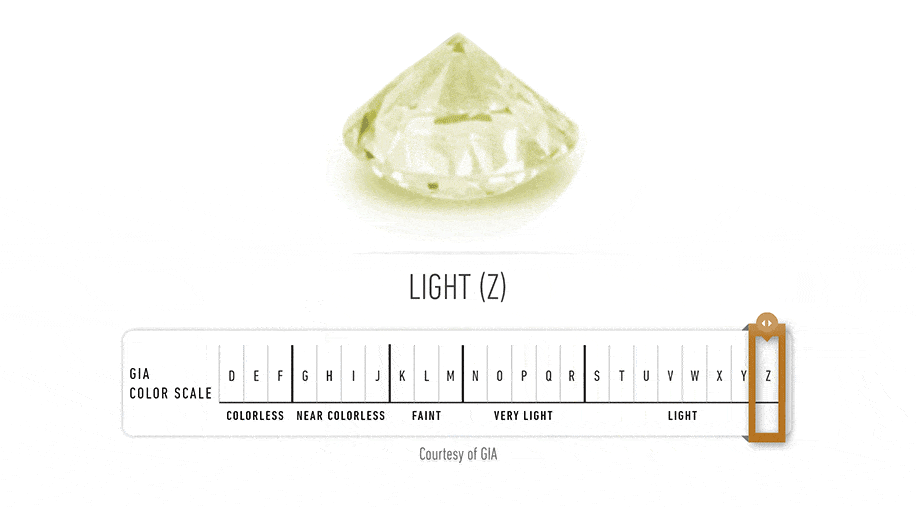
Diamond Color Actually Means Lack of Color The diamond color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is based on the absence of color. A chemically pure and structurally perfect diamond has no hue, like a drop of pure water, and consequently, a higher value. GIA's D-to-Z diamond color-grading system measures the degree of colorlessness by comparing a stone under controlled lighting and precise viewing conditions to masterstones stones of established color value.
GIA's diamond D-to-Z color-grading scale is the industry's most widely accepted grading system. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues, with increasing presence of color, to the letter Z.Many of these color distinctions are so subtle that they are invisible to the untrained eye; however, these distinctions make a very big difference in diamond quality and price.
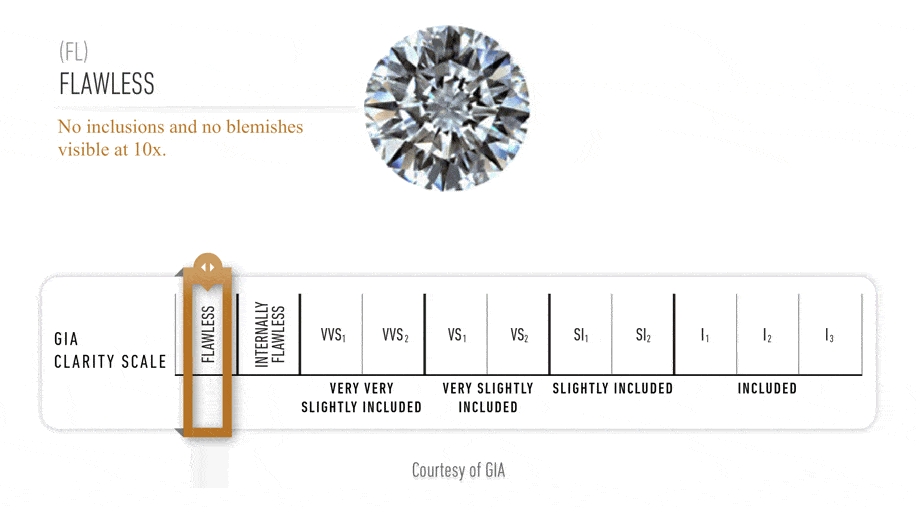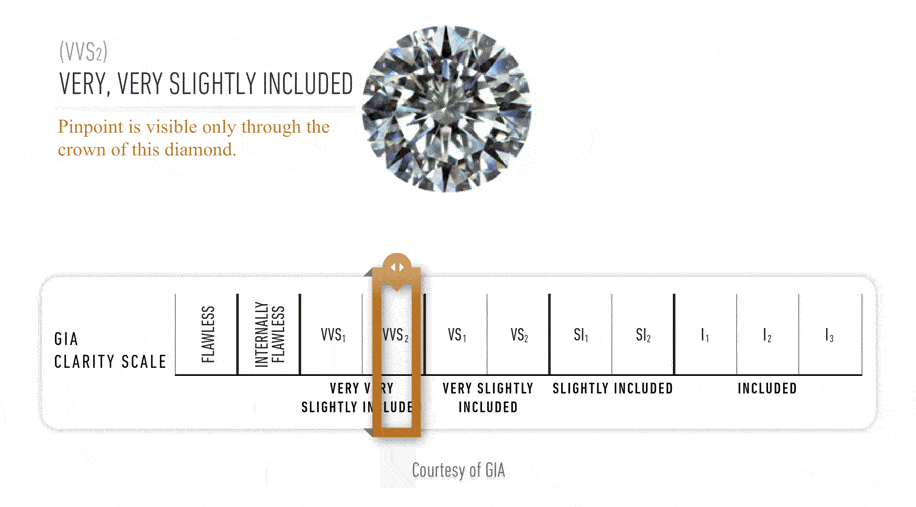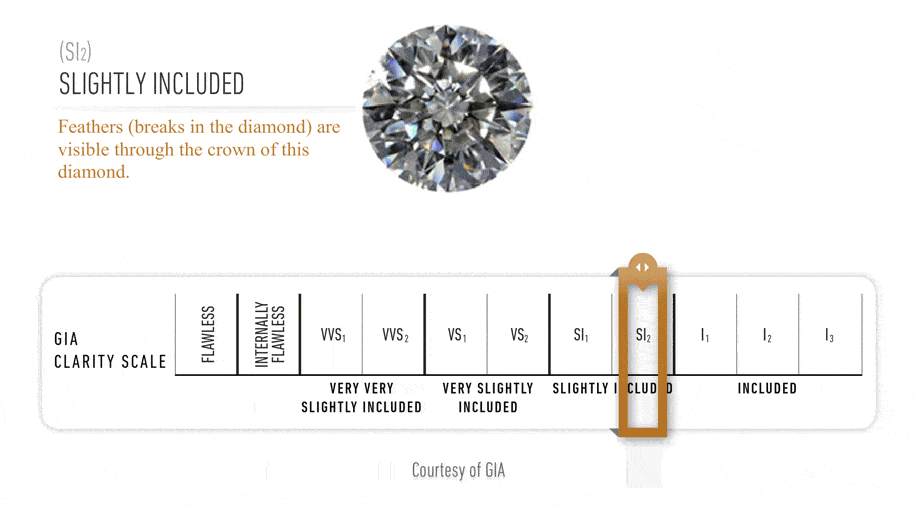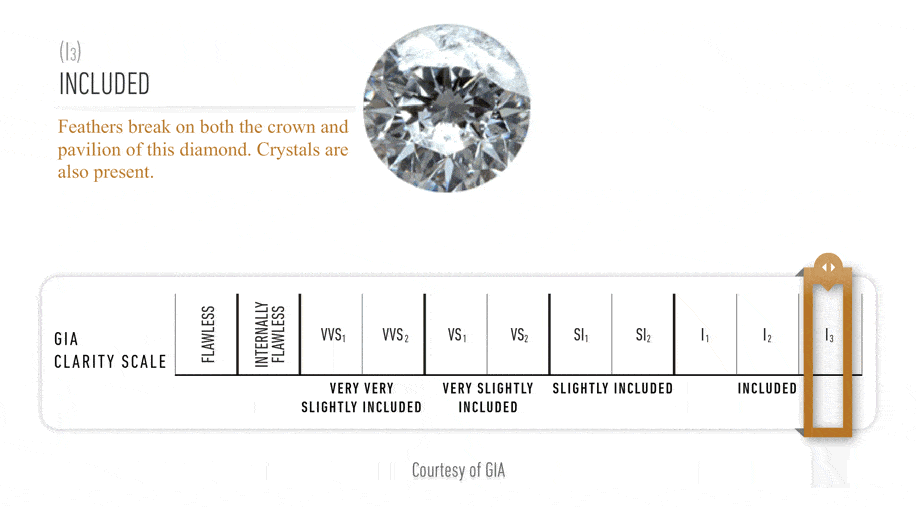
Diamond Clarity Refers to the Absence of Inclusions and Blemishes Natural diamonds
are the result of carbon exposed to tremendous heat and pressure deep in the earth.
This process can result in a variety of internal characteristics called 'inclusions'
and external characteristics called 'blemishes.'
The GIA Diamond Clarity
Scale has 6 categories, some of which are divided, for a total of 11 specific
grades.